If you’re reading this, you’re likely on a quest to find the perfect air compressor for your home garage.
It’s a journey many of us have embarked on, and it’s one that can be filled with more questions than answers:
- What size air compressor do I need?
- What are the benefits of having one in my garage?
- How do I choose the right one?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into these questions and more. We’ll explore the role of air compressors in a home garage, understand the different sizes and their applications, and provide actionable tips to help you make the most of your air compressor.
Let’s get to it!
Air Compressors in Home Garages
The home garage is more than just a place to park your car.
For many of us, it’s a workshop, a sanctuary, and a space where we can work on our projects and hobbies.
And in this space, an air compressor can be an invaluable tool as they can power a variety of tools, from nail guns to paint sprayers.
They work by storing pressurized air in a tank, which can then be used to power tools or inflate tires.
What are their benefits?
They can save you time on tasks, provide more power than manual tools, and even help you achieve a more professional finish on your projects.
But not all air compressors are created equal.
The size and type of air compressor you need will depend on what you plan to use it for.
What Size Air Compressor For Home Garage?
Now that we’ve covered the basics of air compressors and their role in a home garage, let’s delve deeper into the main topic: What size air compressor do you need for your home garage?
In this context, it’s crucial to consider the scale of your applications.
For Light-Duty Tasks
For small-scale applications such as inflating tires, powering brad nailers, or other light-duty tasks, a smaller air compressor might be all you need.
This is because these tasks typically require less air volume, so a compact, portable air compressor with a tank size of around 4-8 gallons should suffice.
These smaller units are also beneficial if you have limited space in your garage or if you need to move the compressor around frequently.
For Medium-Scale Tasks
If you’re into more demanding tasks like running impact wrenches, paint sprayers, or using multiple tools simultaneously (I call these tasks “medium-scale applications”), you’ll need an air compressor with a bit more muscle.
For these circumstances, a compressor in the 10-gallon range is often recommended.
These units provide a balance between portability and power, allowing you to tackle a wider range of tasks without running out of air too quickly.
For Large-Scale Tasks
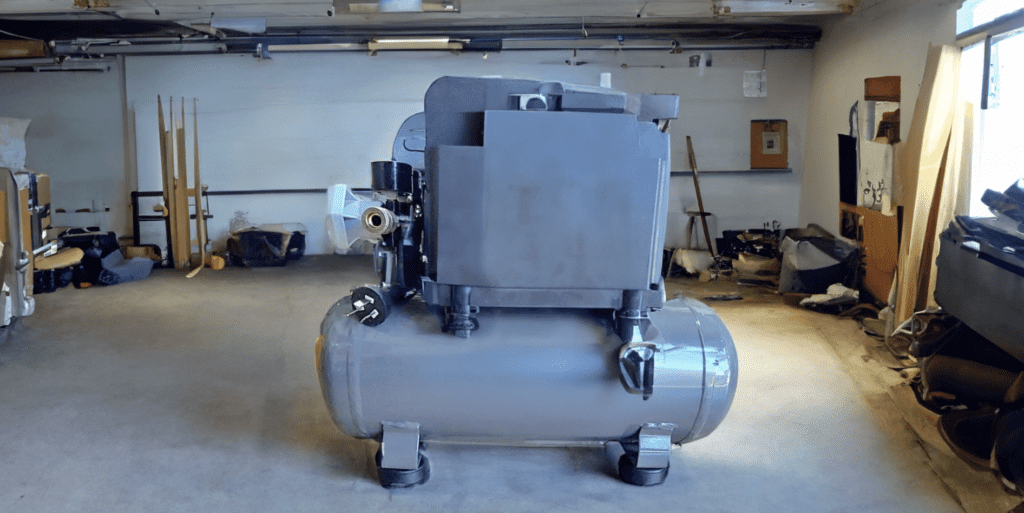
For large-scale applications such as sandblasting, continuous use of high-demand air tools, or if you’re running a professional workshop from your garage, you’ll need a heavy-duty air compressor.
These tasks require a high volume of air, so an air compressor with a tank size of 30-50 gallons or higher is typically recommended. These larger units can deliver the high CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) and PSI (Pounds per Square Inch) needed for these demanding tasks.
Tips For Using Air Compressor For Home Garage
Using an air compressor in your home garage can significantly enhance your DIY capabilities.
However, to get the most out of your air compressor, it’s essential to use it correctly and safely. Here are some tips to help you along the way.
Safety First
Safety should always be your top priority when using an air compressor.
Ensure the compressor is in good working condition before use. Regularly inspect the compressor and its accessories for any signs of wear and tear. Pay particular attention to the hoses and connectors, as these can often be the weak points in the system.
Lastly, never exceed the recommended pressure levels. Overpressurizing your air compressor can lead to dangerous situations, including the risk of the tank bursting. Always adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding the maximum pressure levels.
Proper Maintenance
Air compressors, like any other tool, require regular maintenance to ensure their longevity and optimal performance.
This includes regularly draining the tank to remove any accumulated moisture as moisture in the tank can lead to rust, which can weaken the tank and lead to failure over time.
Check and replace air filters as needed too. Dirty or clogged air filters can reduce the efficiency of your air compressor and lead to increased wear and tear. Regularly cleaning or replacing the filters can help maintain the compressor’s performance and extend its lifespan.
Efficient Setup
The setup of your air compressor can significantly impact its efficiency.
If you’re running air lines in your garage, a linear setup is often best, especially if you intend to have drops on one or two garage walls. This setup allows for easy access and efficient use of the compressor.
Consider the location of your air compressor. It should be placed in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating. Also, ensure there’s enough space around the compressor for easy access for maintenance and operation.
Right Tool for the Job
Air compressors can power a wide range of tools, but it’s crucial to match the tool to the compressor’s capabilities.
Using a tool that requires more CFM or PSI than your compressor can deliver can lead to inefficient operation and potential damage to both the tool and the compressor.
Before using a tool, check its CFM and PSI requirements and ensure your compressor can meet these needs. If you frequently use high-demand tools, consider investing in a larger compressor to meet these requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need an air compressor for my garage?
If you frequently engage in activities that require pneumatic tools, such as inflating tires, painting, sandblasting, or using impact wrenches, an air compressor can be a significant work saver as it provides speed and power from an unlimited energy source – air, making your tasks easy and safe.
However, if your tasks are limited to light-duty work that doesn’t require pneumatic tools, you might not need one.
Is it safe to use an air compressor indoors?
Yes, it is generally safe to use an electric air compressor indoors, but there are some considerations to keep in mind.
Air compressors can generate excessive noise and blow particulates that can be worse indoors.
Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure proper ventilation and use protective gear like ear protection to mitigate these risks.
Gas-powered compressors, on the other hand, should never be used indoors due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning from exhaust fumes.
Are air compressors expensive to run?
The cost of running an air compressor can vary widely based on its size, how often it’s used, and your local electricity rates.
Industrial air compressors used in factories or workshops can consume a significant amount of electricity, especially if they’re operated frequently.
However, smaller air compressors used at home typically consume less power and are therefore less expensive to run. T
he cost of energy can account for up to 75% of the compressor’s life-cycle cost, so understanding what you’re spending to run your compressor is critical when looking for potential savings.



